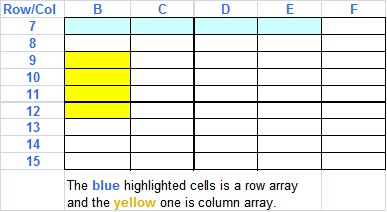
Array Formulas
To enter an array formula you first highlight the necessary cell. Either a column or row.

Once you have highlight the array, leave it highlighted and go to the formula bar (usually at the top) click in the bar and enter the formula. When you are through, instead of pushing enter, press (at once):
<CTRL><SHIFT><ENTER>
at the same time. You will notice that Excel puts {} around the formula and will not let you edit and individual cells in the array. The only way to change it is to highlight and change the formula the same way you entered it or delete all the cells in the array.
Example I
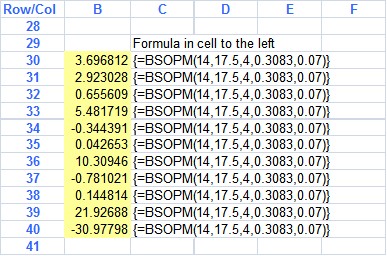
'In this case the array function BSOPM was entered once into the formula bar after highlight cells b35..b45. After pressing CTRL-SHIFT-ENTER the formula was entered into all the cell as an array function (notice the { } ). Below is how the formula bar looked just before being entered into the cells.
![]()
Notice again that the curly brackets are not entered by the user, but are entered automatically when <shift><ctrl><enter> is pushed.
Example II
To us FSMulticorr you must use the function as an array formula. This is a special form of the function/formula in Excel. You can study the Excel Help file to see a general discussion of array formulas. In general you would highlight a row of cells equal to number of rows in the correlation matrix, three in this case. Example 1 below shows the highlight cells and function typed in to the entry area.
Example 1 Example 2
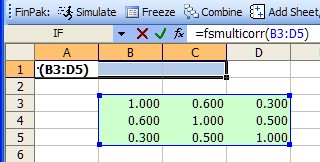
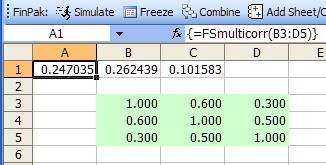
You then entry the formula by simultaneously pressing <shift><ctrl><enter>. If you have successfully done this you will see the curly brackets and the result shown in cells A1:C1 will the three random numbers that are correlated in the way the correlation matrix dictates.
There are row vector array formulas, column vector array formulas and matrix array formulas. For FSMulticorr the optional random number input vector must be a row vector, the output may be either a row or column vector (the example above shows a row output vector).
Copyright © 2009 Pieter Vandenberg